47k ohm resistor is a component widely use in electronics applications. Understanding the characteristics and applications of the 47K ohms resistors is necessary, whether you're working on a DIY electronics project, designing a circuit, or simply learning about electronics. In this blog post, we'll explore the resistor's colour code, types, power ratings watts, dimensions, packing types, tolerance, and FAQs.
47K Resistor Color Code 4 Band and 5 Band
Color | 1st Band | 2nd Band | 3rd Band | Multiplier | Tolerance |
Black | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1Ω | – |
Brown | 1 | 1 | 1 | 10Ω | – |
Red | 2 | 2 | 2 | 100Ω | ±2% (G) |
Orange | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1KΩ | – |
Yellow | 4 | 4 | 4 | 10KΩ | – |
Green | 5 | 5 | 5 | 100KΩ | – |
Blue | 6 | 6 | 6 | 1MΩ | – |
Violet | 7 | 7 | 7 | 10MΩ | – |
Grey | 8 | 8 | 8 | 0.001Ω | – |
White | 9 | 9 | 9 | 0.0001Ω | – |
Gold | – | – | – | 0.1Ω | ±5% (J) |
Silver | – | – | – | 0.01Ω | – |
Resistor colour codes are a standardized system for encoding the value and tolerance. The 47kilo ohms have in both 4-band and 5-band code.
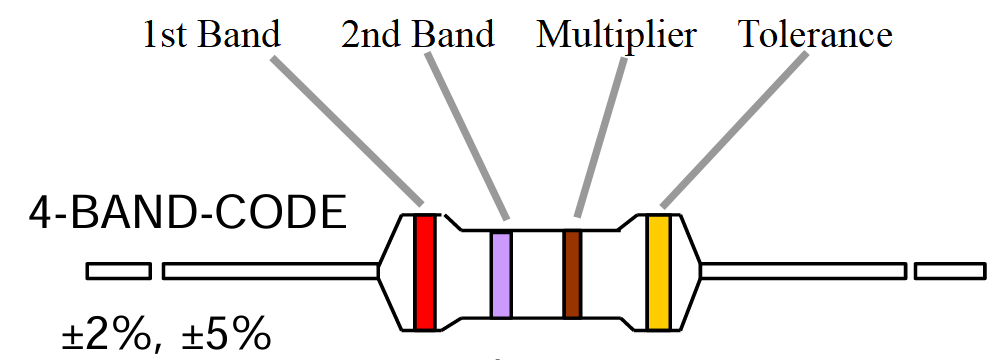
4 Bands Color Code : Yellow-Violet-Orange-Gold (±5% tolerance)
· 1st-Band (4): Yellow
· 2nd-Band (7): Violet
· 3rd-Band (Multiplies by 10³): Orange
· 4th-Band (Tolerance): Gold or Silver (depending on tolerance)
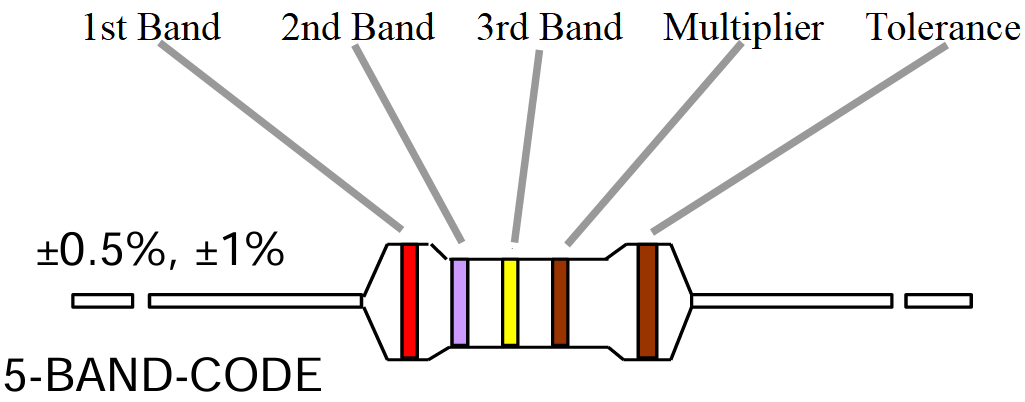
5 Bands Color Code : Yellow–Violet–Black–Red–Brown = 47KΩ ±1%.
· 1st-Band (Yellow) = 4
· 2nd-Band (Violet) = 7
· 3rd-Band (Black) = 0
· 4th-Band (Red multiplier) = ×100
· 5th-Band (Brown tolerance) = ±1%
Value calculation:
· Significant figures: 470
· Multiplier: ×100 → 470 × 100 = 47,000Ω = 47KΩ
Types Of 47K Ohm Resistor
In various types base on the construction and material. Here are some of the most common types:
· Carbon Film Resistor: The most common type, cost-effectiveness and general use in various applications.

· Metal Film Resistor: Better accuracy and stability, lower noise and use in precision circuits.
· Metal Oxide Film Resistor: Improve tolerance and better performance at high temperatures

· Thick Film Resistor: Durable and reliable for most general circuits.
· Wirewound Resistor: Made by winding a wire around a ceramic or metal core. Offer excellent stability and power handling, ideal for high-power applications.
Power Ratings Resistor 47K
Indicates how much power it can dissipate safely without overheating or damaging itself. Here are the common power-wattage:
0.05W(1/20W) | 47k resistor 1 2 watt | 4W | 10.5W |
0.063W(1/16W) | 0.6W | 5W | 11W |
0.1W(1/10W) | 0.7W | 6W | 12W |
0.125W(1/8W) | 0.75W(3/4W) | 6.5W | 14W |
0.167W(1/6W) | 47k 1w resistor | 7W | 15W |
47k ohm 1/4 watt resistor | 1.2W | 7.5W | 20W |
0.3W | 1.5W | 8W | 25W |
0.333W(1/3W) | 2W | 9W | 30W |
0.4W | 3W | 10W | 40W |
Choosing the right power rating ensures your resistor can handle the current without overheating or failing in your circuit.
Size / Dimensions 47K Resistors
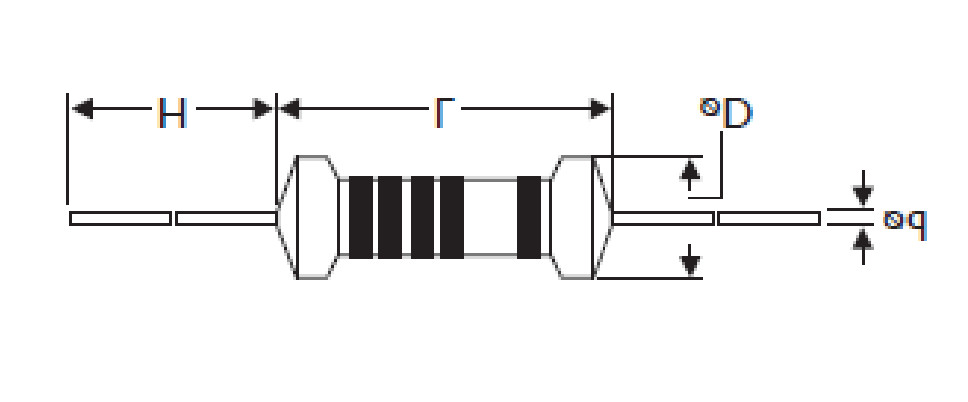
Power Rating | L(mm) | ψD(mm) | H(mm) | ψd(mm) |
0.063W(1/16W) | 2.3~3.0 | 1.2~1.4 | 26~28 | ~0.4 |
1/8W mini 1/4W | 3.4 ± 0.3 | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 28 ± 2.0 | 0.45 ± 0.05 |
1/4W Mini 1/2W | 6.3 ± 0.5 | 2.4 ± 0.2 | 28 ± 2.0 | 0.55 ± 0.05 |
1/2W 1Ws | 9.0 ± 0.5 | 3.3 ± 0.3 | 26 ± 2.0 | 0.55 ± 0.05 |
1W 2Ws | 11.5 ± 1.0 | 4.5 ± 0.5 | 35 ± 2.0 | 0.8 ± 0.05 |
2W 3Ws | 15.5 ± 1.0 | 5.0 ± 0.5 | 33 ± 2.0 | 0.8 ± 0.05 |
The sizes depends on the type and power rating. Generally, resistors come in several standard sizes, with common sizes including:
Power Rating and Size:
· The power rating directly influences the size of the resistor. Higher power ratings require larger sizes and thicker leads to dissipate heat safely.
· Resistors with higher power ratings will have a larger diameter and longer body length to accommodate the higher thermal dissipation.
· Axial lead resistors have the same basic size across different resistance values (e.g., 47000 ohms, 100K ohms, etc.), but the tolerance and power rating primarily determine the size.
Packing Types
Resistors usually package for ease of handling, especially in mass production settings. Common packing types include:
· Tape & Box: Often used for bulk quantities.
· Tape & Reel
· Tray
· Cut Tape: Individually cut from a reel, ideal for small batch orders or prototyping.
Tolerance
Indicates the variation between the stated value and the actual value of a resistor. Here’s the typical range in kilohms:
Tolerance (%) | Range for 47kΩ Resistor |
±0.01% | 46.995kΩ~47.005kΩ |
±0.02% | 46.990kΩ~47.010kΩ |
±0.05% | 46.975kΩ~47.025kΩ |
±0.1% | 46.930kΩ~47.070kΩ |
±0.25% | 46.825kΩ~47.175kΩ |
±0.5% | 46.650kΩ~47.350kΩ |
±1% | 46.530kΩ~47.470kΩ |
±2% | 46.240kΩ~47.760kΩ |
±5% | 44.650kΩ~49.350kΩ |
±10% | 42.300kΩ~51.700kΩ |
±20% | 37.600kΩ~56.400kΩ |
The lower the tolerance, the more accurate the circuit is to its nominal value.
FAQs 47K (47000) Ohm Resistors
1. What color is a 47k resistor?
A 47KΩ resistors typically has the following color codes depending on the number of bands:
· 4-Band Color Code:
Yellow–Violet–Orange–Gold
(47Kohm with ±5% tolerance)
· 5-Band Color Code:
Yellow–Violet–Black–Red–Brown
(47Kohm with ±1% tolerance)
The first two bands indicate the significant digits, the third band is the multiplier, and the fourth (or fifth) band indicates the tolerance.
2. What is a 47 ohm resistor used for?
Commonly use in voltage dividers, signal processing circuits, and applications requiring precise resistance for current limiting, pull-up/pull-down configurations, or filtering.
For the following purposes:
1. Current Limiting: Helps protect components like LEDs by limiting the current flowing through them and prevent damage.
2. Voltage Dropping: Use in series to drop a small amount of voltage across itself.
3. Pull-down/Pull-up : Use to ensure a defined logic level on an input pin of a microcontroller, preventing floating states. Helps ensure a known state for digital inputs by connecting them to ground or Vcc.
4. Damping in Signal Lines: Use to reduce reflections and noise in high-speed or long trace signal lines (e.g., in microcontroller I/O).
5. Biasing Resistors: Use to set the base current for BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor) or FET (Field-Effect Transistor) in amplifier circuits or switching applications.
6. RC Filters (Low-Pass/High-Pass Filters)
Use in combination with a capacitor to form RC filters for signal conditioning, smoothing, or noise reduction.
7. Audio Amplifiers and Tone Control Circuits
In audio applications, use in tonecontrol circuits to filter audio signals
8. Timing Circuits (RC Timing)
In RC timing circuits, a 47000 ohms can pair with a capacitor to create a time delay or to generate clock pulses.
9. Sensor Applications
Use in sensor circuits (e.g., photoresistors, thermistors) to form a voltage divider or in combination with other sensors to modify their output for easier processing.
10. Power Supply Circuits
In voltage regulation circuits, use in feedback loops of voltage regulators to set the output voltage.
It particularly suite for low-impedance applications where a small resistance is needed without significantly altering circuit behavior.
3. What is a 47k ohm resistor equivalent to?
Equivalent to the resistance :
47KΩ (standard shorthand using the metric prefix "k" for kilo, or ×1,000)
47,000 ohms(same value, written in base units)
47,000 ohms ± tolerance.
4.7 × 10⁴ ohms (scientific notation)
Other resistors in parallel or series combinations that total 47kΩ (e.g., two 94kΩ resistors in parallel, or a 22kΩ + 25kΩ resistor in series)
In some cases, resistors in the range of 47k to 50k ohms can use interchangeably, depending on the application.
Functionally, it is equivalent to any configuration that results in a total resistance of 47kΩ.
Read More:
1. What Is The 100K Resistor and colour code?
HOT NEWS
The 0402 Resistor: A Comprehensive Guide

0402 Resistor
2025-05-06
Understanding A 0603 Resistor

0603 resistor,dimensions,marking code, values
2025-05-29
What Is A 1206 Resistor?

1206 resistor dimensions,footprint,value
2025-06-05
MT3608 Boost Converter - An In-Depth Guide
MT3608 Boost Converter
2025-09-04
What is 10k Ohm Resistor?

10k resistor 10k resistor color code
2025-05-14
Everything You Need To Know About ARE1309 Relay

2025-04-23
Guide To The AMS1117 Voltage Regulator

AMS1117 Voltage Regulator Circuit
2025-08-17
What Is The 1K Ohm Resistor?
1k ohm resistor and color code
2025-05-21
Complete Guide to the 220 Ohm Resistor
220 Ohm Resistor
2025-07-28
2512 Resistor - A Comprehensive Guide

2512 Resistor
2025-08-13








 Product Catalog
Product Catalog