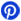
Among the many resistance values available, the 300 ohm resistor stands out as its unique applications and versatile use in various electronic devices. Resistors are one of the most fundamental and widely use components in electronics. Whether you are designing a circuit for current limiting, voltage division, or impedance matching, it play a role in regulating electrical flow. In this post, we’ll explore everything you need to know about the 300 ohm resistors, including its colour codes, types, practical uses, and how to choose the right one for your needs.
1. What is a 300 Ohm Resistor?
2. 300 Ohm Resistor Color Code
4. Resistor 300 Ohms Applications
5. Practical Use Cases of a 300 Ohms Resistor
6. 300 Ohm Resistor vs. Similar Values
7. Selecting the Right 300 Ohm Resistor
8. Frequently Asked Questions About Resistor 300 Ohm
What is a 300 Ohm Resistor?
A type of passive electronic component that provides resistance to the flow of electric current in a circuit. Measured in ohms (Ω), its resistance value is 300-ohms, meaning it resists the flow of electrical current with a factor of 300. 300Ω helps in controlling the voltage and current within a circuit, protecting sensitive components such as LEDs, transistors, and amplifiers. The 300 Ω is particularly useful in circuits that require moderate current limitation or voltage regulation. Also widely use in signal processing, audio circuits, and power distribution systems.
In essence, design the 300 ohm resistor to limit the amount of current passing through a particular part of an electrical circuit, ensuring the device operates safely within its designed parameters. By doing so, it prevents overheating, damage, and possible failure of more delicate components.
300 Ohm Resistor Color Code
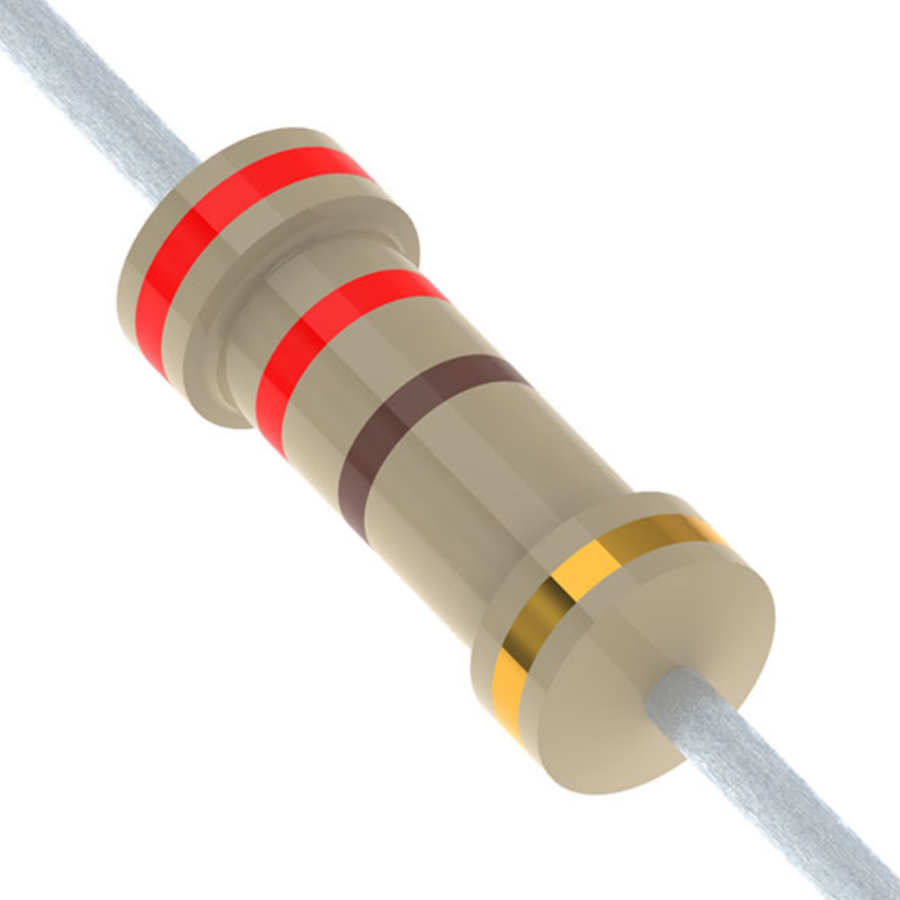
Colour codes are a system that allows you to easily determine the resistance value of a through-hole-resistor by reading the colored bands printed on its surface. The standard color code for a 300-ohm depending on the type of resistor, typically featuring either a 4-band or 5-band code.
Resistor 4 Ring 300 Ohm

Band | Color | Meaning |
1st-Band | Orange | First-digit(3) |
2nd-Band | Black | Second-digit(0) |
3rd-Band | Brown | Multiplier (x10) |
4th-Band | Gold | Tolerance (±5%) |
The first-band is Orange, which represents the digit 3. The second-band is Black, which represents the digit 0. The third-band is Brown, which acts as a multiplier of 10, so you multiply the digits (30 × 10 = 300). The fourth-band is Gold, which represents the tolerance of ±5%. This means the actual resistance value vary by 5% above or below the stated 300 ohms.
Thus, the resistor has a nominal value of 300-ohms, with a tolerance range of 285 to 315 ohms.
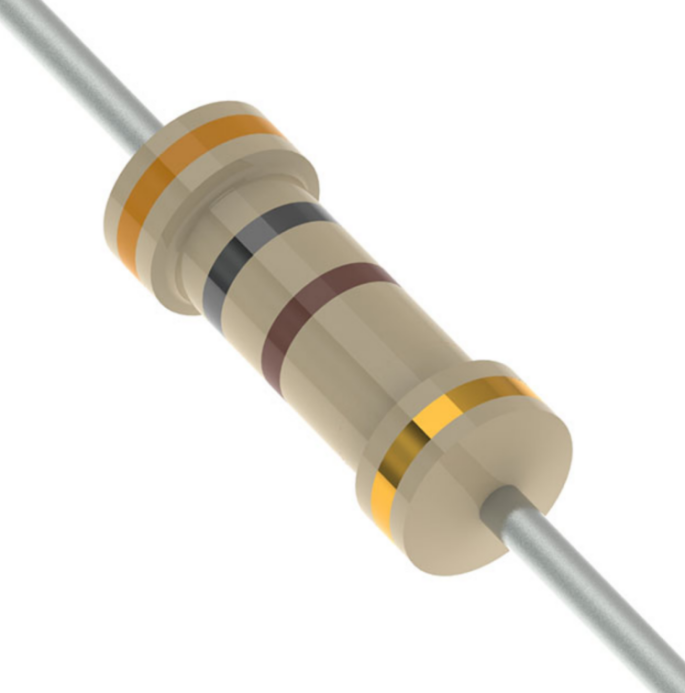
300 Ohm 5 Band Colour Code:
Band | Colour | Meaning |
1st-Band | Orange | First-digit(3) |
2nd-Band | Black | Second-digit (0) |
3rd-Band | Black | Third-digit (0) |
4th-Band | Black | Multiplier (x1) |
5th-Band | Brown | Tolerance (±1%) |
The first-band is Orange, which represents the digit 3. The second-band is Black, which represents the digit 0. The third-band is Black too, which represents the digit 0. The fourth-band is Black, which acts as a multiplier of 1, so you multiply the digits (300 × 1 = 300). The fifth-band is Brown, which represents a tolerance of ±1%, meaning the actual resistance vary by 1% above or below the stated 300-ohm.
Thus, the resistor has a nominal value of 300 ohm, with a tolerance range of 297 to 303 ohms.
Types of 300 Ohm Resistors
300 ohms come in various types, each suited to different applications depending on the material, construction, and power requirements.
Through-Hole Resistors
Through-hole package is the most common type and use when the resistor needs to insert manually into a circuit board. These resistors are available in several types, including:
Carbon Film: These are cost-effective and commonly use in basic circuits where precision is not the highest priority. This type is widely available and easy to use.
Metal Film: Offering higher accuracy and stability than carbon-film, prefer metal film resistors in applications where need tighter tolerances, such as precision signal processing.
Wire-Wound: Construct by winding a metal wire around a core. They are highly accurate and capable of handling higher power ratings. A good example is the resistor RX21-6 300 ohm , which is a varnished wire-wound type. Often use for high-power applications, such as amplifiers.

300 Ohm SMD Resistor
Surface-Mount Device (SMD) resistors design for automated assembly and often use in compact or high-density circuit boards. SMD type is much smaller than through-hole package and are ideal for modern electronics, especially where space constraints are a concern. For 300-ohm SMD, they come in different sizes and tolerances, making them suitable for various consumer electronics, communication devices, and portable gadgets.
The materials used in SMD resistors include thin and thick film technologies, with tolerances typically ranging from ±1% to ±5%. Also come with different power ratings, such as 0.25W, 0.5W, and 1W, allowing designers to select the appropriate component based on their application.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Wire-wound resistors tend to be more accurate and durable but are bulkier, while carbon and metal film types are smaller and cheaper, though metal film prefer for their precision. On the other hand, SMD resistors are highly compact and ideal for high-density circuits but require specialized equipment for installation.
Resistor 300 Ohms Applications
The 300-ohms use in a variety of applications to control current, voltage, and impedance. Commonly find in signal processing circuits, where it helps regulate signal flow by ensuring proper voltage levels and preventing overloads. This is important for maintaining signal integrity and accuracy in systems that require precise signal conditioning.
In audio circuits, 300 ohm resistors are useful for impedance matching, ensuring maximum power transfer between components such as amplifiers, speakers, and microphones. By matching impedances, these components help minimize signal loss and distortion, contributing to clear and accurate sound reproduction in audio systems.
Another significant application is in LED circuits, where use 300 ohms for current limiting. LEDs are sensitive to current, and using a 300Ω in series with the LED ensures that it does not receive too much current, which will damage the component. This is necessary for maintaining the LED’s longevity and optimal performance.
In voltage divider circuits, use 300 Ω to split a higher voltage into a lower, usable value. This is especially useful when different parts of a circuit require different voltage levels. By combining the 300 Ω with another resistor, designers can set specific voltage drops necessary for other components, such as sensors or transistors.
For power supply circuits, 300Ω resistors help regulate current flow, ensuring that components do not receive excessive current or voltage. This prevents damage and ensures that the power supply operates efficiently. They also use to bias transistors or regulate the voltage at certain points in the circuit.
In amplifiers and filters, 300 ohm play a key role in stabilizing circuits and controlling frequency responses. They are use in feedback loops within amplifiers to maintain a stable output, and in filter circuits to ensure that only desired frequencies pass through while blocking others.
In communication systems, 300 ohm use for impedance matching between transmitters, receivers, and antennas. This ensures that transmit the signal efficiently without reflection or loss, which is useful in systems such as radio transmission or networking equipment.
Practical Use Cases of a 300 Ohms Resistor
LED Current Limiting
LEDs require specific current values to function correctly, and the resistors 300 ohms plays a key role in limiting that current. By selecting a circuit with the appropriate resistance, you ensure the current through the LED does not exceed its rated maximum, which will lead to overheating or permanent damage. For example, in a simple circuit with a 9V power supply and a standard LED, the 300 ohm ensures the LED operates safely and efficiently.
Audio Line Matching
In audio equipment, can use a 300 ohm resistor to match impedance between two devices, such as a speaker and an amplifier. Impedance matching helps prevent signal loss, ensuring that transfer audio signals effectively and with minimal distortion.
Simple Amplifier Circuits
In small audio or radio amplifier circuits, can use for biasing or voltage division. This helps ensure that the amplifier operates at optimal efficiency, providing clear sound output without distortion.
300 Ohm Resistor vs. Similar Values
Resistor Value | Typical Application | Current Restriction | Effect on Circuit |
100 Ohm | LED, voltage dividers | Low current | More current flow, low-power |
220 Ohm | LED, signal attenuation | Moderate current | Common for LED, moderate flow |
250 Ohm | LED, signal conditioning | Slightly more restriction | Small current control |
300 Ohm | Audio circuits | Moderate current | Balanced current control |
330 Ohm | Audio, signal processing | Less restriction | Allows slightly more current |
Comparing a 300 ohm resistor to similar resistance values can give you a sense of how it fits into various applications. A 100 Ohm resistor, for example, allow more current to flow, making it suitable for low-power, high-current applications. A 220 Ohm resistor restrict current even more, making it ideal for lower voltage circuits.
On the other hand, a 330 ohm resistor is similar to the 300-ohm version but is better suited for higher voltage applications, where you need a slight reduction in current. The choice of resistor depends largely on the application’s specific voltage and current requirements.
In summary, a 300 ohm resistor provides a balanced resistance level, making it suitable for applications where need moderate current limiting and voltage regulation.
Selecting the Right 300 Ohm Resistor
When selecting a 300-ohm, it is important to consider factors such as power rating, tolerance, resistor type, and temperature coefficient. Wattage rating indicates how much power the resistor can dissipate without overheating.
Here’s the information on 300 ohm with different power ratings:
300 Ohm 1/4 Watt Resistor: Use in low-power circuits where require minimal current. Suite for small electronic circuits that don’t need significant power dissipation.
300 Ohm 1/2 Watt Resistor: Commonly in general-purpose circuits that require moderate current and power handling. Typically use in everyday electronics where the power demands are not too high.
300 Ohm 2 Watt Resistor: Ideal for applications where involve a bit more power, such as audio amplifiers or higher-power circuits that require more resistance and power handling capabilities.
300 Ohm 5 Watt Resistor: Use in circuits with higher power demands, such as power supplies, amplifiers, or systems where moderate power dissipation is necessary.
300 Ohm 10 Watt Resistor: This type suites for circuits where require significant power dissipation, like high-power amplifiers or industrial applications. It can handle larger currents and provides better heat management.
18W 300 Ohm Power Resistor: Design for industrial power systems and heavy-duty applications where need high energy dissipation. Use in environments that demand stable and reliable power handling.
300 Ohm 75 Watt Resistor: Common in high-power applications, especially in industrial systems where substantial heat dissipation is necessary. 75W build to handle large power loads in heavy-duty circuits.
Each power rating indicates how much energy the resistor can safely dissipate without overheating, and the right choice depends on the specific power requirements of your circuit.
The tolerance of the resistor determines how accurately it can provide the required resistance value. For applications requiring high precision, you need choose for a resistor with a tolerance of ±1%, ±0.05%, ±0.02%, ±0.01% or ±0.005%.
Resistor Type
Determine its construction and performance characteristics. Common types include:
Carbon Film, Metal Film, Wire-Wound Resistors.
Physical Form Factor: Through-Hole vs. Surface Mount
Through-Hole Resistors: Have leads that insert through holes in the circuit board and solder into place. They are larger and easier to handle manually, making them suitable for DIY projects and low-volume production. They also offer better power dissipation in many cases and commonly use in high-power applications.
Surface-Mount Resistors (SMD): These packages are compact and design for automated assembly on circuit boards. Commonly use in modern, high-density electronic devices, such as mobile phones, computers, and automotive electronics. They are ideal for space-constrained designs but not handle power dissipation as well as through-hole resistors in high-power circuits.

Temperature Coefficient
Indicates how much the resistance value changes with temperature. A circuit with a low-temperature coefficient will experience minimal resistance change as the temperature fluctuates, making it more stable in environments with varying temperatures.
Standard Resistors: These have a temperature coefficient that vary from ±100 ppm/°C to ±200 ppm/°C (parts per million per degree Celsius).
Precision Resistors: For applications that require high stability, such as precision signal processing or instrumentation, prefer resistors with a low temperature coefficient (around ±25 ppm/°C to ±50 ppm/°C). They maintain their resistance over a wide temperature range.
Frequently Asked Questions About Resistor 300 Ohm
What is 300 ohm resistor price and where to buy?
The price of 300 ohms resistors typically ranges from a few cents to a few dollars, depending on the type (carbon film, metal film, wire-wound, etc.), power rating, and quantity. Bulk purchases usually offer a lower unit price. You can buy from electronic component suppliers such as Orwintech Electronic, or online marketplaces like Amazon and eBay. Local electronics stores also carry them. Prices vary based on brand, quality, and shipping, but for small quantities, they are generally inexpensive.
What color is a 300 ohm resistor?
A 300-ohm typically has a 4-band or 5-band colour code. For the 4-band code, the colors are Orange (3), Black (0), Brown (multiplier x10), Gold (tolerance ±5%). For the 5-band version, the color coding is Orange (3), Black (0), Black (0), Black (multiplier x1), Brown (tolerance ±1%). These colors represent the resistor's resistance value and tolerance. The exact color bands differ slightly based on manufacturer standards, but Orange and Black are consistent across both versions.
What is the voltage drop across a 300 ohm resistor?
The voltage drop across a 300 Ohm resistor depends on the current passing through it. According to Ohm's Law, the voltage drop calculate by multiplying the current by the resistance. For example, if 1 amp of current flows through a 300-ohm resistor, the voltage drop will be 300 volts. The voltage drop can vary depending on the specific circuit configuration, the current flow, and the power supply. Need to know the current in the circuit to calculate the exact voltage drop across the resistor.
Are there SMD (Surface Mount Device) 300 ohm resistors available?
Yes, SMD 300 Ohm resistors are available. This package is compact, designed to mount directly onto a circuit board without leads. Commonly use in modern, high-density electronics as their small size and ability to place using automated assembly processes. They come in various sizes, such as 0402, 0603, 0805, 1206, and 2512. These are perfect for applications where space is limited, and need to assemble components quickly and efficiently.
What does a 300 ohm resistor do?
A 300 Ohm resistor primarily limits or controls the flow of current in a circuit. Use to set specific voltage drops, control current levels, and protect sensitive components like LEDs, transistors, or integrated circuits. Also use in impedance matching in audio circuits, signal processing, and various other applications where require precise resistance. By choosing the correct resistance value, the 300-ohm helps ensure that the circuit operates within safe electrical parameters, preventing overcurrent and ensuring proper functionality of other components.
What power rating is necessary for a 300 ohm resistor in a specific application?
The power ratings of a 300 ohms resistor depends on the application’s current and voltage. In general, resistors come in 1/4, 1/2, 2 watt, or higher ratings. For low-power circuits, 0.25 watt is usually sufficient. However, in high-power applications, such as audio amplifiers or power supplies, you will need a 2-watt, 5-watt, or even 10-watt resistor. The power rating ensures that the resistor can dissipate heat without overheating. Always choose a power rating that exceeds the power expected to prevent failure and ensure long-term reliability.
Is there a 300 ohm resistor?
Yes, 300 Ohm resistors are available and commonly use in electronic circuits. They typically use for current limiting, impedance matching, or signal conditioning. 300-ohm is a standard resistance value, and you can find it in both through-hole and SMD (surface mount) types. These resistors come in various power ratings, tolerances, and materials, such as carbon film, metal film, and wire-wound. Use in a wide range of applications, from audio circuits to power supplies, and can purchase from various electronic component suppliers.
Why do you need a 300 ohm resistor for the LED?
A 300-ohms resistor commonly use in LED circuits for current limiting. LEDs have a fixed voltage drop, and without a current-limiting resistor, excessive current will flow through the LED, potentially damaging or burning it out. It helps control the amount of current flowing through the LED, ensuring it operates within its specified current rating. This resistor value balances between providing adequate brightness while preventing overcurrent, which can shorten the lifespan of the LED. It's essential for protecting the LED from damage while ensuring reliable performance.
How does temperature affect a 300 ohm resistor?
The resistance of a 300-ohm can change with temperature. This is because the temperature-coefficient, a property that determines how much a resistor's value changes as the temperature varies. For most resistors, the resistance increases with higher temperatures. If the temperature rises too much, the resistor will experience thermal runaway, where its resistance continues to increase, potentially causing circuit failure. To mitigate this, use precision resistors with low temperature coefficients in circuits that require stability over a wide range of temperatures, such as in sensitive sensors or high-precision equipment.
How to verify the value of a 300 Ohm resistor?
To verify the value of a 300 ohm, you can use a digital multimeter (DMM). Set the multimeter to measure resistance (Ω), and connect the leads to either end of the resistor. The multimeter will display the resistance value. If the resistor is within tolerance, the reading should be close to 300-ohms. For example, a resistor with ±5% tolerance should read between 285 and 315 Ohms. This method provides a quick and easy way to check the resistor's actual value before using it in a circuit.
In conclusion, the 300 Ohm resistor plays a key role in many electronic circuits. It helps control current, limit power flow, and protect sensitive components like LEDs, transistors, and integrated circuits. Whether use for current limiting, impedance matching, or signal conditioning, it ensures circuit stability and prevents damage to parts. When selecting a 300 ohms resistors, it's important to consider the resistor type, power ratings, and temperature coefficient to meet the specific needs of your application. Understanding its characteristics will help ensure efficient and reliable circuit performance.
Read More:
1. Guide to the 3 Ohm Resistor: Specifications and Color Code
HOT NEWS
The 0402 Resistor: A Comprehensive Guide

0402 Resistor
2025-05-06
Understanding A 0603 Resistor

0603 resistor,dimensions,marking code, values
2025-05-29
What Is A 1206 Resistor?

1206 resistor dimensions,footprint,value
2025-06-05
MT3608 Boost Converter - An In-Depth Guide
MT3608 Boost Converter
2025-09-04
What is 10k Ohm Resistor?

10k resistor 10k resistor color code
2025-05-14
Everything You Need To Know About ARE1309 Relay

2025-04-23
Guide To The AMS1117 Voltage Regulator

AMS1117 Voltage Regulator Circuit
2025-08-17
What Is The 1K Ohm Resistor?
1k ohm resistor and color code
2025-05-21
Complete Guide to the 220 Ohm Resistor
220 Ohm Resistor
2025-07-28
2512 Resistor - A Comprehensive Guide

2512 Resistor
2025-08-13








 Product Catalog
Product Catalog