100 ohm resistor is a fundamental component in electronics. Serving to regulate current flow, divide voltages, and protect sensitive components. Its moderate resistance value makes it versatile for various applications, from signal conditioning to power management.

Catalog
Features of 100 Ohms Resistor
Power Rating of 100 Ohm Resistors
100 Ohm Resistor Color Code
Dimensions
Types of Resistors
Tolerance in 100 Ohm Resistors
Packaging of axial Resistors
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for 100 Ohms Resistors
Features of 100 Ohm Resistor
1. Resistance Value: 100 ohms.
The resistor has a nominal resistance of 100 ohms. It limits current flow in a circuit according to Ohm’s Law (V = IR). A standard value and widely use in both analog and digital circuits. For current limiting, voltage division, and signal conditioning.
2. Power Rating: Commonly in 1/4W, 1/2W, 1W, and 2W.
It indicates the maximum power the resistor can safely dissipate without damage or degradation. These ratings—ranging from 0.25 watts to 2 watts. Can select base on the thermal and electrical requirements of the application.
3. Tolerance: ±0.005%, ±0.01%, ±0.02%, ±0.05%, ±0.1%, ±0.25%, ±0.5%, ±1%, ±2%, ±5%, ±10%, ±20%.
This defines the allowable variance from the nominal 100 ohms resistance. Use precision resistors (e.g., ±0.005%) in critical applications such as instrumentation. General-purpose resistors (e.g., ±5% or ±10%) suffice in less sensitive circuits. The tighter the tolerance, the higher the accuracy and consistency in performance.
4. Material Composition: Constructed from carbon film, metal film, or wire-wound materials. Each offering different performance characteristics.
5. Packaging: Supply packaging Carbon film resistors normally taped in 'ammo' boxes. Other styles maybe supplied on request. All tape specifications are in accordance with IEC 286-1.
Bag, Box, Tray, Tube, Tape &Reel, Tape &Box
6.RoHS compliant, REACH compliant, lead free and halogen free
7. Low Cost –High Reliability- High power tosize ratio -Flame retardant coatings standard.
Power Rating of 100 Ohm Resistors
The power rating signifies the maximum energy the resistor can handle without overheating:
0.05W (1/20W) | 0.063W (1/16W) | 0.1W (1/10W) | 0.125W(1/8W) |
0.167W (1/6W) | 0.175W | 0.2W (1/5W) | 0.25W(1/4W) |
0.3W | 0.333W (1/3W) | 0.4W | 1/2 watt 100 ohm resistor |
0.6W | 0.667W (2/3W) | 0.75W (3/4W) | 100 ohm 1 watt resistor |
1.2W | 1.25W | 1.5W | 1.7W |
1.75W | 1.8W | 2W | 2.25W |
2.3W | 2.5W | 2.7W | 3W |
3.2W | 3.25W | 3.5W | 3.75W |
4W | 4.5W | 5W | 5.25W |
5.5W | 6W | 6.5W | 7W |
7.5W | 8W | 9W | 10W |
10.5W | 11W | 12W | 13W |
13.5W | 14W | 15W | 16W |
17W | 20W | 25W | 30W |
35W | 40W | 50W | 60W |
70W | 100W | 140W | 150W |
1/4 Watt: For low-power signal circuits.
1/2 Watt: Slightly higher power applications.
1 Watt and Above: Use higher dissipation in power supplies and amplifiers .
Selecting the appropriate power rating ensures reliability and prevents thermal failure.
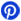
100 Ohm Resistor Color Code
Resistors use color bands to denote their resistance value and tolerance:
4-Band Code: Brown (1), Black (0), Brown (×10), Gold (±5% tolerance) — representing 100 ohms.
5-Band Code: Brown (1), Black (0), Black (0), Black (×1), Gold (±5% tolerance) — also indicating 100 ohms.
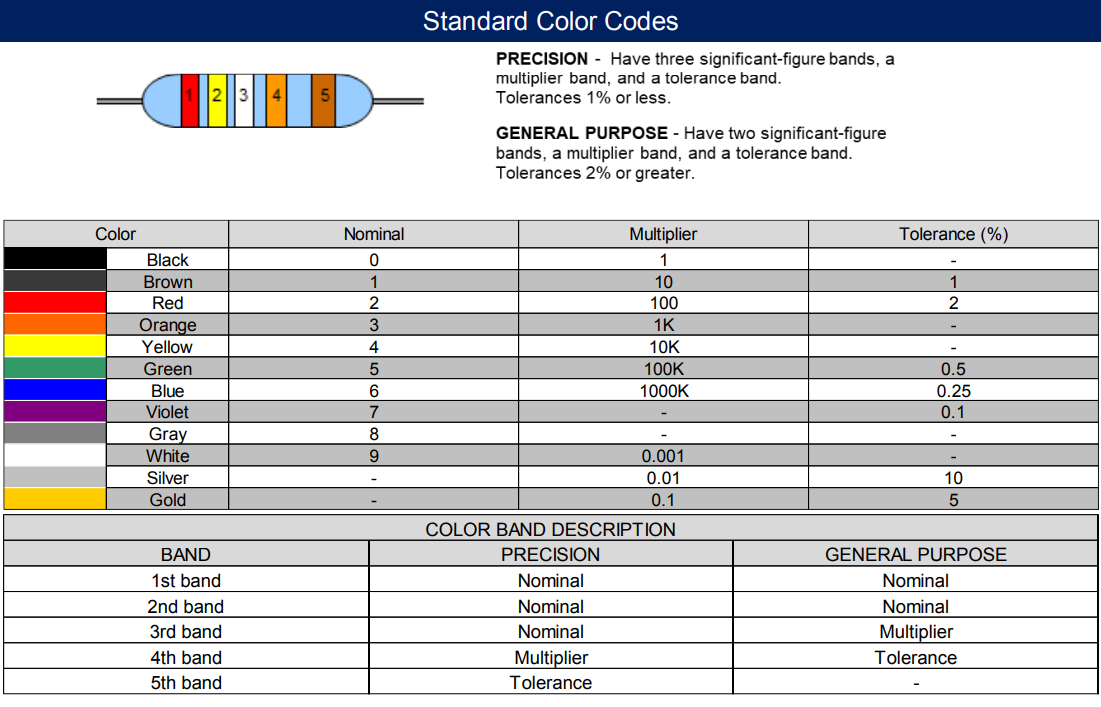
Dimensions
Through-Hole (Axial Leaded) Resistors.
These are the most common for general-purpose applications. Dimensions depend mainly on the power rating:
Power Rating | L (mm) | ψD (mm) | H (mm) | ψd (mm) |
1/8W | 3.3±0.2 | 1.8± 0.2 | 28 ± 2.0 | 0.45 ± 0.05 |
1/6W | 3.4 ± 0.3 | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 28 ± 2.0 | 0.45 ± 0.05 |
1/4W | 6.3 ± 0.5 | 2.4 ± 0.2 | 28 ± 2.0 | 0.55 ± 0.05 |
1/3W | 6.8 ± 0.5 | 2.5 ± 0.2 | 28 ± 3.0 | 0.55± 0.05 |
0.4W | 6.3 ± 0.5 | 2.4 ± 0.2 | 28 ± 2.0 | 0.55 ± 0.05 |
1/2W | 9.0 ± 0.5 | 3.3 ± 0.3 | 26 ± 2.0 | 0.55 ± 0.05 |
1W | 11.5 ± 1.0 | 4.5 ± 0.5 | 35 ± 2.0 | 0.8 ± 0.05 |
2W | 15.5 ± 1.0 | 5.0 ± 0.5 | 33 ± 2.0 | 0.8 ± 0.05 |
3W | 15.5 ± 1.0 | 5.0 ± 0.5 | 33 ± 2.0 | 0.8 ± 0.05 |
These are typical dimensions for carbon or metal film resistors. Slight variations may occur depending on manufacturer.
Types of 100 Ohm Resistors
1. Carbon Film Resistors: Economical, suitable for general-purpose applications. With higher noise and lower precision.
2. Metal Film Resistors: Stability, lower noise, and tighter tolerance. Better for precision circuits.
3. Wire-Wound Resistors: Handle higher power levels, use in power supplies and motor controls. Are bulkier and have inductive properties.
Carbon Composition | Carbon Film | Wirewound |
Cement Ceramic | Metal Film | Thin Film |
Metal Foil | Metal Oxide Film | Thick Film |
Compare of the types
Type | Construction & Material | Key Characteristics | Typical Applications |
Carbon Composition | Made from a mixture of carbon powder and resin, molded into a cylindrical shape | Low cost, good surge handling, but poor stability and high noise | Vintage equipment, surge applications |
Carbon Film | Carbon deposited on an insulating substrate | Better tolerance and stability than carbon composition, moderate noise | General-purpose electronics |
Wirewound | Resistance wire (e.g., nichrome) wound around a ceramic core | High power ratings, excellent precision and stability, but inductive | Power supplies, audio circuits, high-precision applications |
Cement/Ceramic | Typically a wirewound resistor encased in a cement-coated ceramic housing | High power dissipation, flameproof, durable under harsh conditions | Power resistors, motor control, industrial equipment |
Metal Film | Metal layer (often nickel-chromium) deposited on a ceramic rod | High precision, low noise, good temperature stability | Audio gear, instrumentation, precision analog circuits |
Thin Film | Ultra-thin metal layer on ceramic or glass substrate | High accuracy and stability, excellent temperature coefficient | High-end electronics, medical devices, aerospace |
Metal Foil | Resistor element made from a foil of metal glued to a substrate | Extreme precision, ultra-low temperature coefficient, minimal noise | Metrology, high-precision measuring instruments |
Metal Oxide Film | Metal oxide (e.g., tin oxide) deposited on ceramic | High temperature and voltage tolerance, flame-resistant | High-voltage applications, automotive, medical |
Thick Film | Thick resistive paste printed on ceramic substrates | Used in SMD resistors, cost-effective, decent performance | Consumer electronics, SMD circuits, mass production |
Summary Chart by Performance
Resistor Type | Precision | Power Handling | Stability | Noise | Cost |
Carbon Composition | ✦ | ✦✦✦ | ✦ | High | Low |
Carbon Film | ✦✦ | ✦✦ | ✦✦ | Moderate | Low |
Wirewound | ✦✦✦ | ✦✦✦✦ | ✦✦✦ | Low | Medium |
Cement/Ceramic | ✦✦ | ✦✦✦✦ | ✦✦ | Low | Medium |
Metal Film | ✦✦✦ | ✦✦ | ✦✦✦ | Low | Medium |
Thin Film | ✦✦✦✦ | ✦✦ | ✦✦✦✦ | Low | High |
Metal Foil | ✦✦✦✦✦ | ✦✦ | ✦✦✦✦✦ | Ultra Low | High |
Metal Oxide Film | ✦✦ | ✦✦✦ | ✦✦✦ | Low | Medium |
Thick Film | ✦✦ | ✦✦ | ✦✦ | Moderate | Low |
Tolerance in 100 Ohm Resistors
Tolerance indicates the permissible variation from the nominal resistance:
±0.005%, ±0.01%, ±0.02%, ±0.05%, ±0.1%, ±0.25%, ±0.5%, ±1%, ±2%, ±5%, ±10%, ±20%
Packaging of 100 Ohm Resistors
1. Axial-Leaded: Traditional cylindrical resistors with leads on both ends. Suit for breadboarding and through-hole PCB assembly.
2. Surface-Mount (SMD): Rectangular components mounted directly onto PCB surfaces. Allow for high-density circuit designs.
The choice depends on the application, assembly method, and space constraints.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
FAQ 1 :What does 100 ohm resistor do?
100-ohm resistor limits current flow, divides voltages. Also provide a specific resistance in a circuit to protect components .
Common Functions of a 100 Ohm Resistor:
1.Current Limiting
Prevents too much current from flowing into sensitive components. Such as LEDs, transistors, or ICs.
Example: Use in series with an LED to prevent it from burning out.
2.Voltage Division
When use in a voltage divider circuit. It helps generate a specific voltage level from a higher voltage source.
3.Impedance Matching
Use in signal lines or transmission lines (such as coaxial cables or Ethernet) . To match impedance and reduce signal reflection or distortion.
4.Pull-Up or Pull-Down Resistors
Can ensure logic inputs are at known states (HIGH or LOW) when no active signal is present.
5.Heat Dissipation
By converting excess electrical energy into heat. It can protect circuits from overcurrent conditions (within its power rating).
6.Filtering and Timing
Works with capacitors or inductors to form filters, delay circuits, or timers in analog and digital applications.
FAQ 2: How to read 100 ohm resistor?
100 ohm resistor typically uses colored bands to indicate its resistance value.
Standard 4-Band Color Code for 100 Ohms:
Band | Color | Meaning |
1 | Brown | 1 (1st digit) |
2 | Black | 0 (2nd digit) |
3 | Brown | ×10 (multiplier) |
4 | (e.g. Gold) | ±5% (tolerance) |
This is incorrect: 100 × 10=1000 ohms.
Identify the color bands: Brown (1), Black (0), Brown (×10) — equating to 100 ohms. The fourth band indicates tolerance, e.g., Gold for ±5%.
100 × 1 = 100 ohms
So, Brown–Black–Brown–Gold = 100Ω ±5%
FAQ 3 : How to test 100 ohm resistor?
Use a digital multimeter set to the resistance (ohms) mode. Connect the probes to each end of the resistor. A reading close to 100 ohms confirms functionality.
Steps to Follow:
Turn off power to the circuit (if the resistor is installed).
Remove the resistor from the circuit if possible . In-circuit testing can give inaccurate results because parallel components.
Set multimeter to resistance (Ω) mode.
For 100 ohm resistor, use the 200Ω or 2kΩ range on the meter.
Connect the multimeter probes:
Touch one probe to each lead of the resistor (polarity doesn't matter for resistors).
Read the display:
The multimeter should read close to 100 ohms.
Allowable range depends on tolerance:
For ±5% tolerance → valid range = 95 to 105 ohms
For designing and troubleshooting electronic circuits. Understanding the specifications and applications of 100-ohm resistors is crucial.
HOT NEWS
The 0402 Resistor: A Comprehensive Guide

0402 Resistor
2025-05-06
Everything You Need To Know About ARE1309 Relay

2025-04-23
What is 10k Ohm Resistor?

10k resistor 10k resistor color code
2025-05-14
120 Ohm Resistor- Specifications, Applications, and Features

2025-05-12
What is 100 Ohm Resistor And Color Code?

100 ohm resistor color code
2025-05-17








 Product Catalog
Product Catalog